
Is going to school for esthetician worth it?
Aesthetician school value depends on program quality, local job market, career commitment, and business development efforts post-graduation.
Articles, Training Resources & Industry Insights for Medical Professionals

Aesthetician school value depends on program quality, local job market, career commitment, and business development efforts post-graduation.
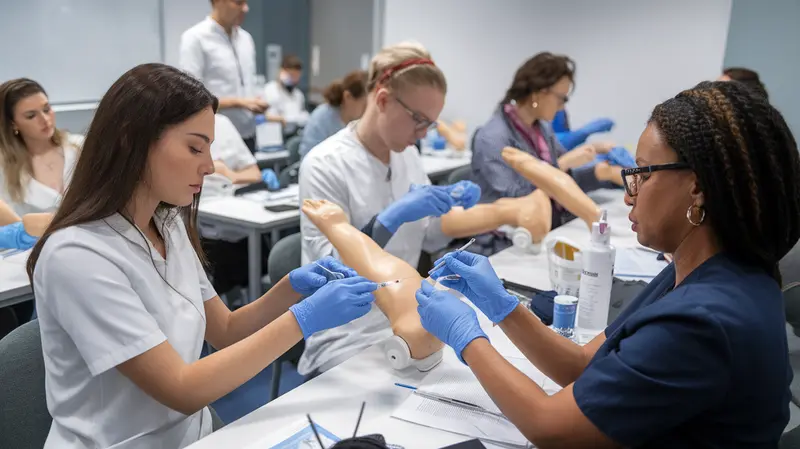
Regular practice is essential for skill development. Most practitioners benefit from ongoing supervised cases before working independently.
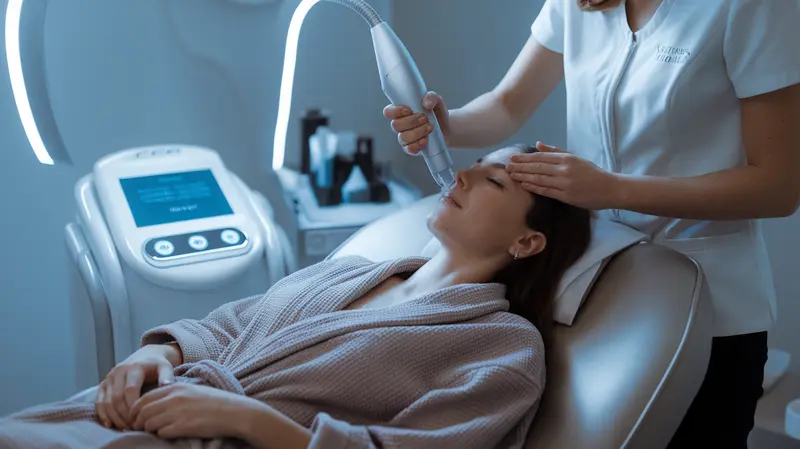
Aesthetician income varies widely based on location, specialization, employment setting, and business model. High earners exceed $70,000 annually.

Evaluate Botox training programs by checking accreditation, instructor credentials, hands-on components, class size, and graduate reviews.
Aesthetician compensation varies by employer. Options include hourly wages, service commission, flat fees per treatment, or combinations.
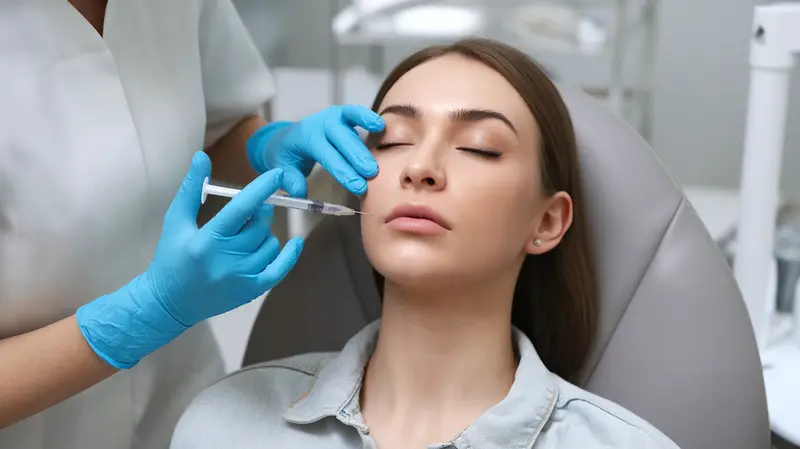

Qualified aesthetician timeline is 4-12 months depending on state hour requirements (600-1,500 hours) and program format.
Techniques include standard injection, microbotox, serial puncture, linear threading, and area-specific approaches for different facial zones.

Qualified filler providers include dermatologists, plastic surgeons, and trained nurses or physician assistants with appropriate credentials.
Makeup application is covered in most aesthetician programs. Depth of training varies by school curriculum and state requirements.

Certification renewal requirements vary by provider. Many require continuing education credits annually or biannually to maintain credentials.
Adding Botox can expand patient services, attract new clients, increase revenue, and provide additional treatment options in your practice.
Self-employed aestheticians need licensure, business registration, liability insurance, equipment, marketing strategy, and client acquisition systems.
Aesthetic.Education | The Next Step in Medical Learning