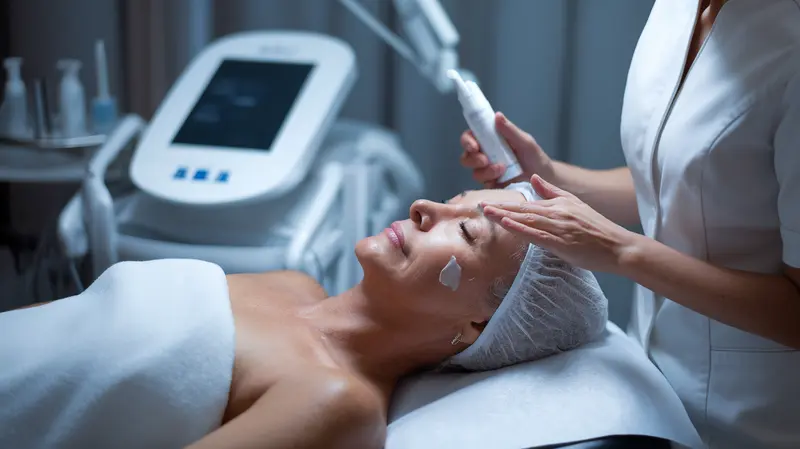
Who makes more, an esthetician or an aesthetician?
Esthetician and aesthetician are the same profession with different spellings. Earnings depend on location and specialization, not spelling.
Articles, Training Resources & Industry Insights for Medical Professionals

Esthetician and aesthetician are the same profession with different spellings. Earnings depend on location and specialization, not spelling.
Some programs offer mentorship pairing new practitioners with experienced injectors for guidance and professional development support.
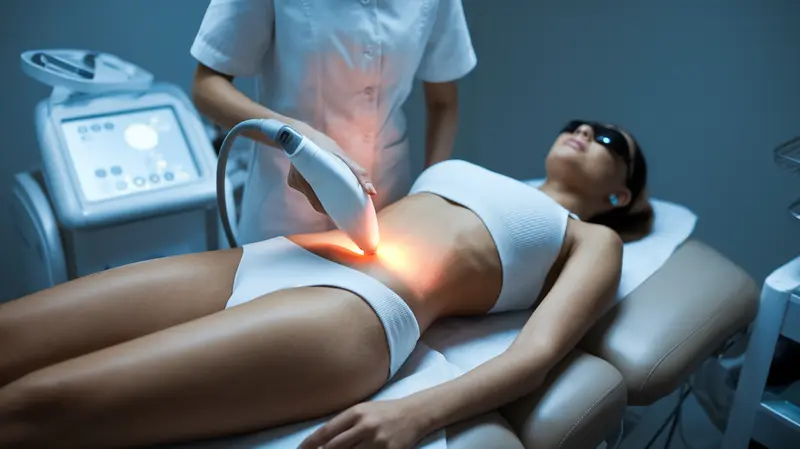
Yes, licensed aestheticians can perform microneedling in most states. Training covers technique, safety protocols, and contraindications.

Sculptra downsides include multiple treatment sessions needed, delayed results (2-3 months), potential nodules, and higher total cost.
Completion rates vary by program. Research specific provider outcomes and student satisfaction before enrollment.

Yes, beginner Botox courses exist for licensed medical professionals new to aesthetic injections. They cover fundamentals and basic techniques.

Some Botox courses include marketing and business development modules. Coverage varies by program focus and target audience.

Yes, physician-specific Botox courses exist with advanced content on pharmacology, dosing protocols, and integration with medical services.

Slowest months for aestheticians typically include January-February and late summer. Holiday seasons and spring are often busiest.
Cosmetology requires more training hours but covers broader services. Aesthetician focuses on skincare. Income depends on specialization and market.
Dermal filler courses typically last 1-5 days depending on program depth, hands-on practice hours, and certification requirements.
Neuromodulators include Botox, Dysport, Xeomin, and Jeuveau. They differ in formulation, onset, spread, and duration characteristics.
Aesthetic.Education | The Next Step in Medical Learning